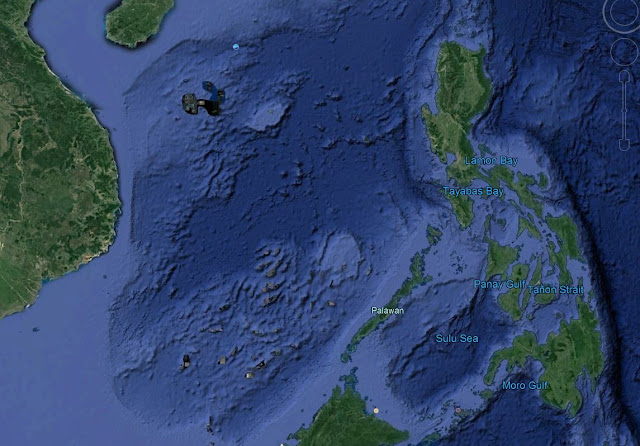
What is Dangerous Ground in South China sea
Dangerous ground is shallow area which consists of many low islands, atool, sand bars, sunken reefs, with reefs rising abruptly from 1000m water depth. It is located NW of Sabah, the total area is around 160,000 sq miles.
Dangerous ground is thought to be the mid ocean ridge where seafloor spreading starts to occurs.
Examination of seafloor magnetic lineations indicates that the SCS oceanic basin opened between magnetic anomalies (polarity chrons) 11 and 5C, which respectively correspond to the geologic times 30 Ma and 16.6 Ma, according to the Gradstein et al. (2004) geologic time scale, or 32–16 Ma according to the older version. These data further show that the ocean basin opened in at least two major phases. During phase I, from 30 Ma to ~21 Ma, the seafloor spreading was north to south, with the spreading ridge striking east-west, and as a result the continental block containing the present North Palawan Island, Reed Bank, Macclesfield Bank and Paracel Islands was separated from the South China continental block to the north. At magnetic anomalies 7-6B (between 24.9 and 21.75 Ma) the spreading ridge jumped to a north-east–south-west trend, with the seafloor spreading in a north-west–south-east direction, which eventually separated Reed Bank from Macclesfield Bank.
Examination of seafloor magnetic lineations indicates that the SCS oceanic basin opened between magnetic anomalies (polarity chrons) 11 and 5C, which respectively correspond to the geologic times 30 Ma and 16.6 Ma, according to the Gradstein et al. (2004) geologic time scale, or 32–16 Ma according to the older version. These data further show that the ocean basin opened in at least two major phases. During phase I, from 30 Ma to ~21 Ma, the seafloor spreading was north to south, with the spreading ridge striking east-west, and as a result the continental block containing the present North Palawan Island, Reed Bank, Macclesfield Bank and Paracel Islands was separated from the South China continental block to the north. At magnetic anomalies 7-6B (between 24.9 and 21.75 Ma) the spreading ridge jumped to a north-east–south-west trend, with the seafloor spreading in a north-west–south-east direction, which eventually separated Reed Bank from Macclesfield Bank.
The area is poorly charted due to making it dangerous to navigate.
It is called dangerous ground due to all neighboring countries (Philipines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, China and Taiwan) partly claimed the area.
Why the fuss over “Dangerous Ground”? Natural resources are a big piece of it. According to current U.S. estimates, the seabed beneath the Spratlys may hold up to 5.4 billion barrels of oil and 55.1 trillion cubic feet of natural gas. On top of which, about half of the world’s merchant fleet tonnage and nearly one third of its crude oil pass through these waters each year. They also contain some of the richest fisheries in the world.
Mischief reef and Sierra Madre are reefs located at Spratly island within Dangerous Ground area. Chinese has made Mischief Reef as their military outpost which is around 20 miles NW of Sierra Madre reef. Sierra Madre is the military outpost for Philippines.
The Chinese has occupied an island with an airstrip near Subi reef.







Comments